类风湿性关节炎(Rheumatoid Arthritis, RA)是一种慢性自身免疫性疾病,主要影响关节,但也可能影响全身其他部位。此病的特点是对称关节炎,导致关节肿胀、疼痛、僵硬和功能受限,如果不治疗,可能导致关节畸形和不可逆的损伤。
【未解决的临床问题】
-
早期诊断:RA的早期诊断仍具挑战性,因为早期症状可能与其他疾病相似。早期诊断对于防止关节损伤和提高治疗效果至关重要。
-
个体化治疗:尽管有多种治疗方法,如DMARDs(疾病改变抗风湿药物)、生物制剂和皮质类固醇,但患者对这些治疗的反应差异很大。需要更多的生物标志物来指导个体化治疗。
-
长期管理:RA的长期管理复杂,涉及药物治疗、物理治疗和生活方式调整。患者需要持续的监测和治疗调整,以应对疾病的波动和潜在的副作用。
-
治疗耐药性和副作用:随着治疗的持续,一些患者可能发展出对特定治疗的耐药性,或遭受严重副作用。研发新的治疗方案以解决耐药问题和减少副作用是迫切需要的。
综合上述信息,类风湿性关节炎的治疗需要综合考虑药物疗法、生活方式调整和定期监测,以提高治疗效果,减轻症状,并改善患者的生活质量。
未来的研究需集中在改进早期诊断技术、发展个体化治疗策略和新型治疗药物的研制上。
我们仅对美国国立卫生研究院(NIH)资助的在研类风湿性关节炎相关项目进行梳理,希望给同仁们的选题思路提供一点启发。
2024年,以“Rheumatoid Arthritis”为检索词、在题目中进行检索,美国NIH针对类风湿性关节炎的在研有78项。
一,谁获得了这些研究?
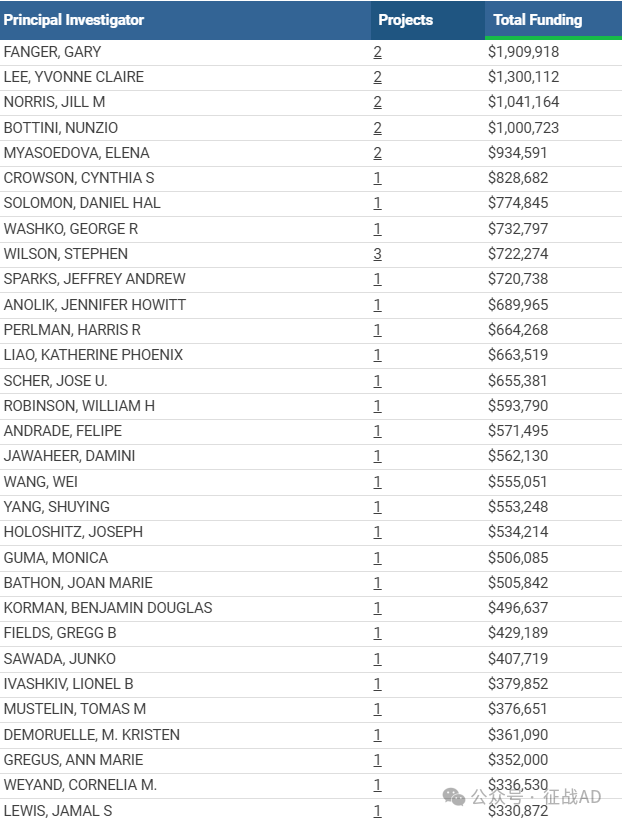
1,在研类风湿性关节炎基金最多的PI
-
RISE THERAPEUTICS, LLC 的 FANGER, GARY
-
NORTHWESTERN UNIVERSITY AT CHICAGO 的 LEE, YVONNE CLAIRE
-
UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO DENVER 的 NORRIS, JILL M
-
CEDARS-SINAI MEDICAL CENTER 的 BOTTINI, NUNZIO
-
MAYO CLINIC ROCHESTER 的 MYASOEDOVA, ELENA
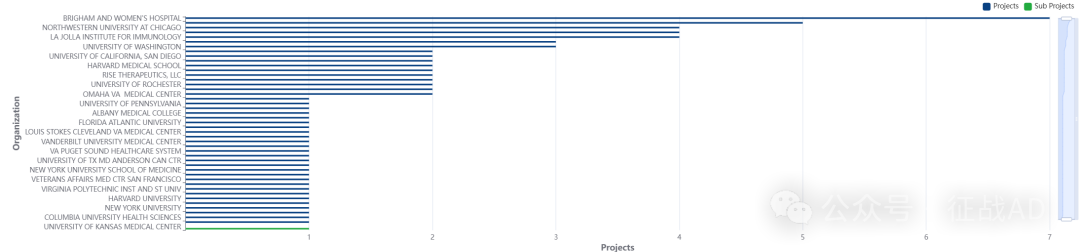
2,类风湿性关节炎基金最多的研究机构
-
布莱根妇女医院
-
芝加哥西北大学
-
罗切斯特梅奥诊所
-
RISE THERAPEUTICS
-
科罗拉多大学丹佛分校等
二,类风湿性关节炎研究热点是什么?
类风湿性关节炎研究领域总览(根据关键词)
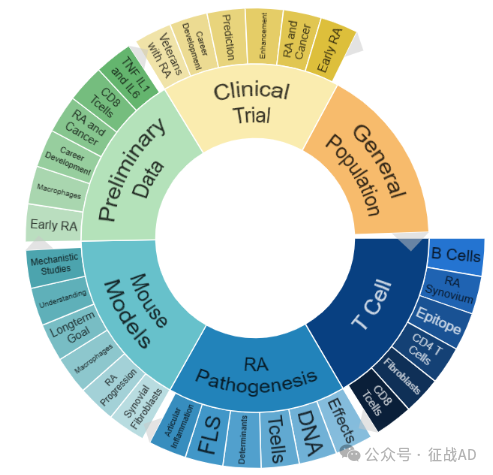
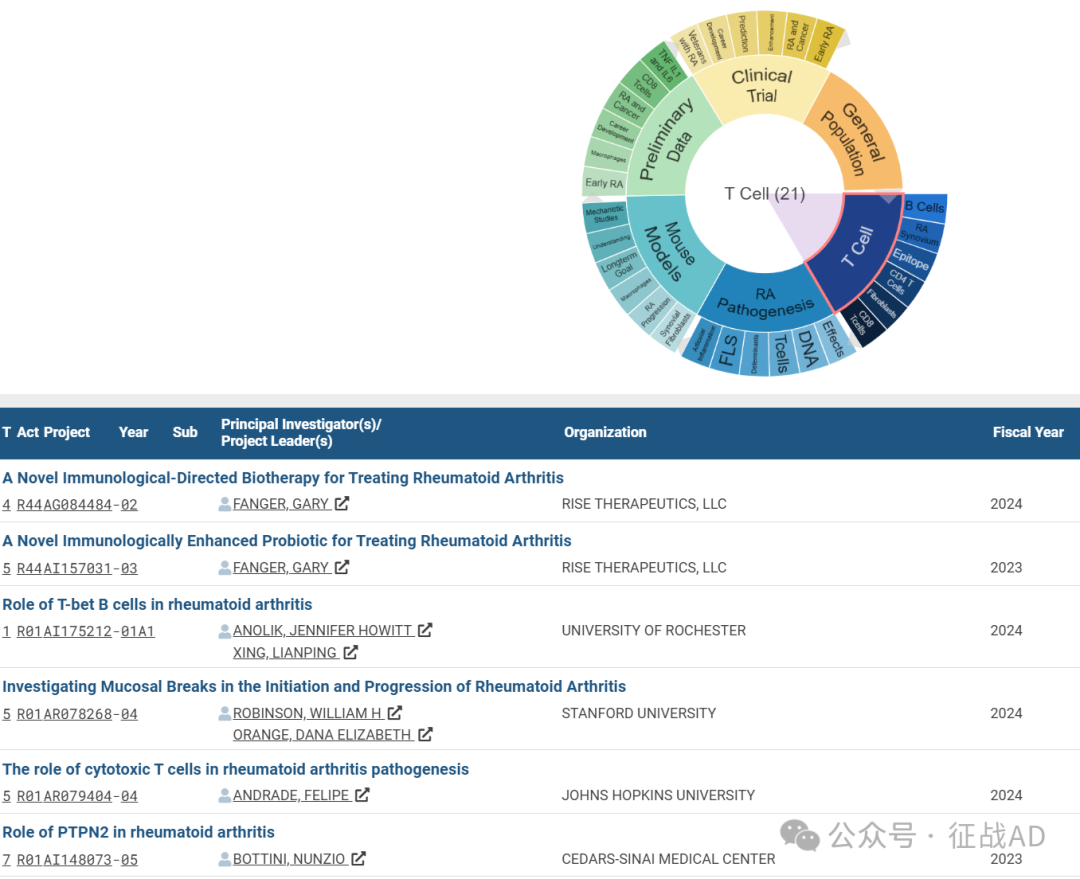
A,关于T细胞(T Cell)的研究项目最多
有 21 项在研基金涉及到了T细胞,关注最多的方面包括B细胞(B Cell)、RA 滑膜(RA Synovium)、表位(Epitope)、CD4 T细胞(CD4 T Cells)、成纤维细胞(Fibroblasts)、CD8 T细胞(CD8 T Cells)等方面研究。
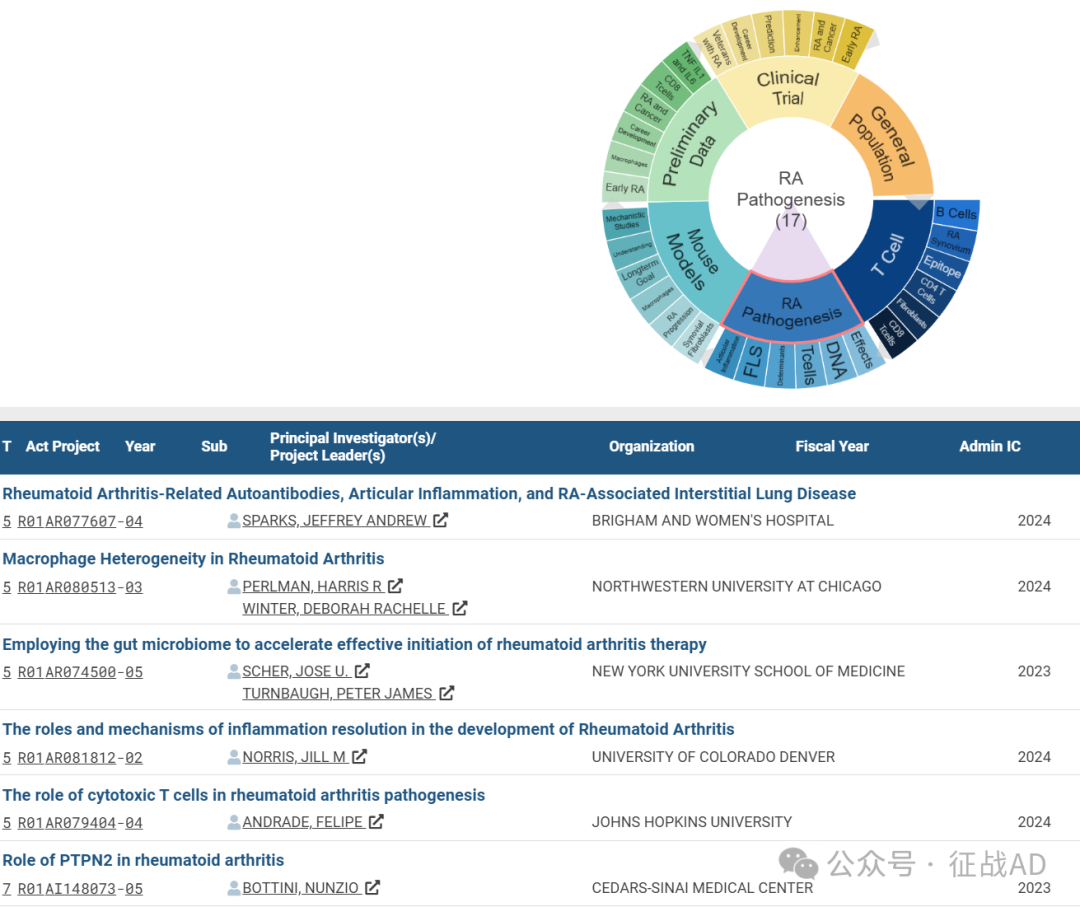
B,RA 发病机制(RA Pathogenesis)的研究
有 17 项研究涉及到RA 发病机制,研究领域主要涉及疗效(Effects)、DNA、T细胞(T Cells)、决定因素(Determinants)、FLS、关节炎症(Articular Inflammation)等方面研究。
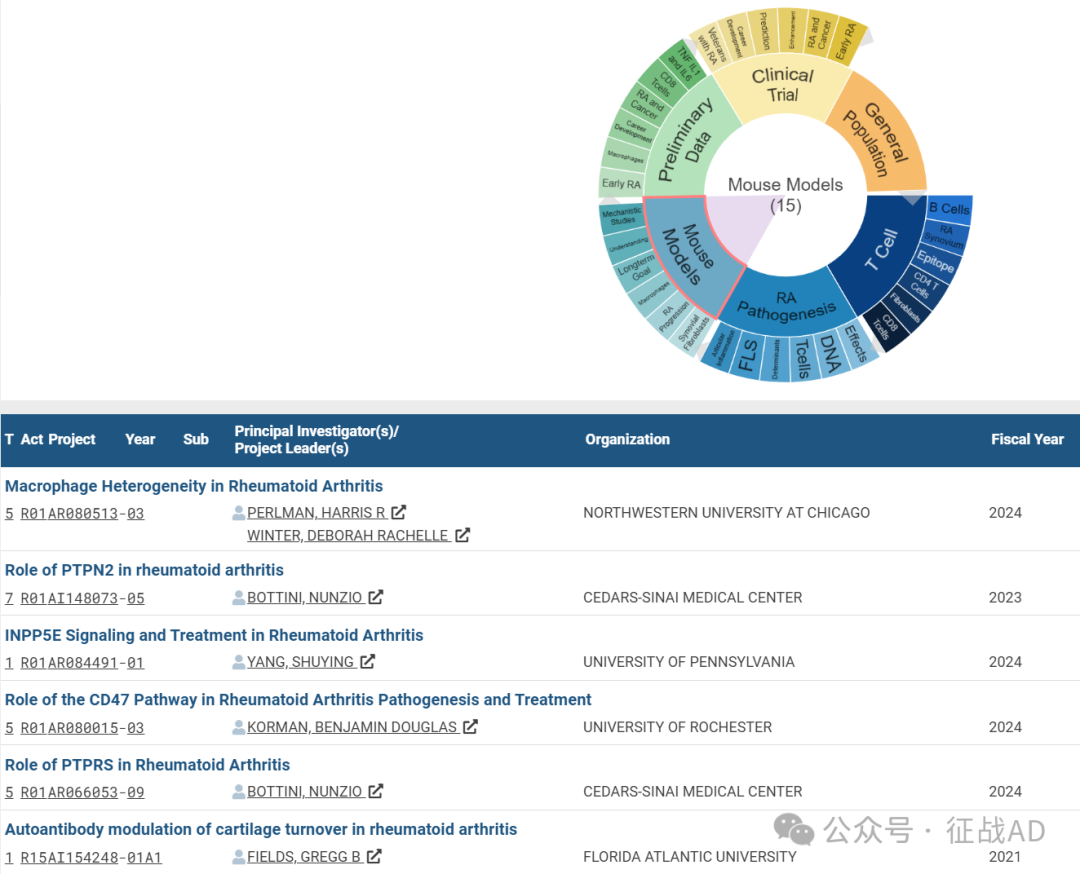
C,小鼠模型(Mouse Models)
有 15 项研究涉及到小鼠模型,涉及的关键词包括如机理研究(Mechanistic Studies)、了解(Understanding)、长期目标(Longterm Goal)、巨噬细胞(Macrophages)、RA 进展(RA Progression)、滑膜成纤维细胞(Synovium Fibroblasts)等。
其他类风湿性关节炎研究大的方向也包括初步数据(Preliminary Data)、临床试验(Clinical Trails)、总人数(General Population)等。
三,借鉴与突破
我们也分享在类风湿性关节炎领域的几项课题摘要,希望对同仁们有所启发。
A,CNS Pain Mechanisms in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis: Implications for the Acute to Chronic Pain Transition
The long-term goal of this research program is to design interventions to prevent pain centralization, and hence chronic pain, in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The objective is to identify modifiable clinical factors and neurobiological pathways that lead to the development of chronic pain in early RA. The focus of this application is early RA because the first 12 months after RA diagnosis likely represents a critical time in which to prevent the acute to chronic pain transition. Preliminary data from the Canadian Early Arthritis Cohort (CATCH) showed that the incidence of fibromyalgia, the prototypical centralized pain condition, is highest during the first year after RA diagnosis. The central hypothesis is that sleep problems, psychosocial factors, and abnormal CNS (e.g., brain, spinal cord) regulatory mechanisms predict the development of pain centralization in the first year after RA diagnosis.
The central hypothesis will be tested by pursuing the following three specific aims:
1) to identify modifiable factors that predict symptoms of pain centralization in early RA;
2) to identify quantitative sensory testing (QST) evidence of augmented CNS pain processing that predict symptoms of pain centralization;
and 3) to define the functional and anatomic brain pathways underlying pain centralization in early RA.
For the first aim, 534 early RA patients from CATCH and CATCH- US (US extension of CATCH) will be enrolled to complete measures of sleep, pain, psychosocial factors, and disability administered at 0, 3, 6 and 12 months after entry into the cohorts.
For the second aim, 125 early RA patients will undergo QST, a type of testing that involves assessing response to well-defined, quantifiable painful stimuli (e.g., pressure and cold), at 0, 3 and 12 months.
For the third aim, 95 patients from Aim 2 will undergo magnetic resonance imaging at 0 and 12 months to assess neuroimaging markers (e.g., correlations in activity between different brain regions, volume of tissue in brain areas consisting of nerve cell bodies) that have previously been shown to be involved in pain centralization.
The proposed research is innovative because it represents a substantive departure from the status quo by: 1) focusing on early RA, 2) incorporating assessments of pain-related constructs into two multi-site early RA registries, and 3) employing a multimodal approach, including patient-reported measures of pain, QST, and neuroimaging, to assess pain pathways.
The proposed research is significant because it will set the stage for intervention design (e.g., cognitive behavioral therapy to treat sleep problems, early treatment of pain with gabapentin) and future trials to prevent chronic pain, ultimately leading to a paradigm shift in the management of pain in systemic inflammatory diseases.
B, A Novel Immunological-Directed Biotherapy for Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis
Our goal is to develop a novel, immunological-directed L. lactis probiotic-based therapeutic for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
We are developing an oral immunotherapy that regulates auto-Ag-specific regulatory T cells (Tregs) to provide bystander tolerance. The two main goals of this approach are: 1) to “switch off” the immune response against the host’s own tissues and 2) balance the effector cell relationships to prevent relapses of chronic inflammation.
This Fast Track application is focused on obtaining human validation for R-2487 by completing a first-in-human Phase 1 RA proof-of-concept clinical trial. The Specific Aims are:
1) finalize R-2487 clinical supply packaging,
2) prepare and file an IND with the FDA,
3) complete a Phase 1 proof-of-concept clinical trial,
4) analyze patient samples before/after dosing to evaluate pharmacodynamic changes and biomarkers,
5) perform Phase 2 clinical manufacturing scale up development to ready R-2487 for larger confirmatory trial.
Successful commercialization of R-2487 will provide a profound medical advancement for treating RA.