有一种疼痛可能和女性的相关性更大,涉及上臂、肩部和胸部,由于肩带的运动而恶化,其特征是间歇性钝痛、灼痛或灼热。
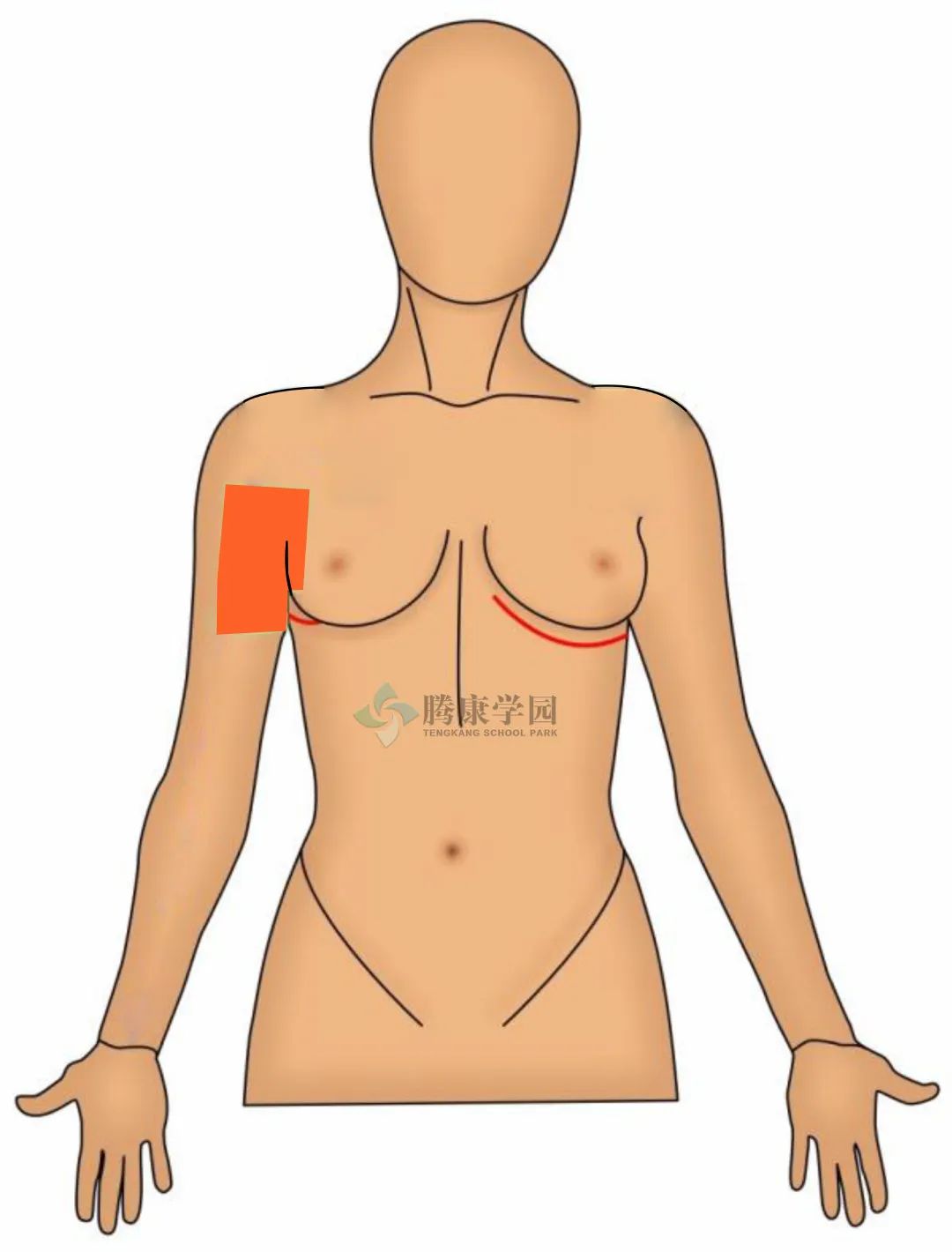
常发生于女性的乳房术后,被称为肋间臂神经卡压综合征。这种疼痛已成为乳腺癌生存的常规问题,对生活质量、身体机能具有重大影响。
超过 20% 至 60% 的乳腺癌患者在接受乳腺癌手术后会继续经历持续性疼痛。
与腋窝相关的手术都有可能损伤到这一条皮神经,比如腋窝淋巴结清扫、前哨淋巴结活检和乳房切除术等常见手术造成的。
肋间臂神经
肋间臂神经是一条皮神经,为胸部外侧、上臂内侧和腋窝提供感觉。
肋间臂神经通常起源于第二肋间神经(T2 脊髓水平)的外侧皮支,它在腋中线刺穿肋间肌和前锯肌,穿过腋窝到达手臂内侧,并与来自手臂内侧皮神经的细丝连接。
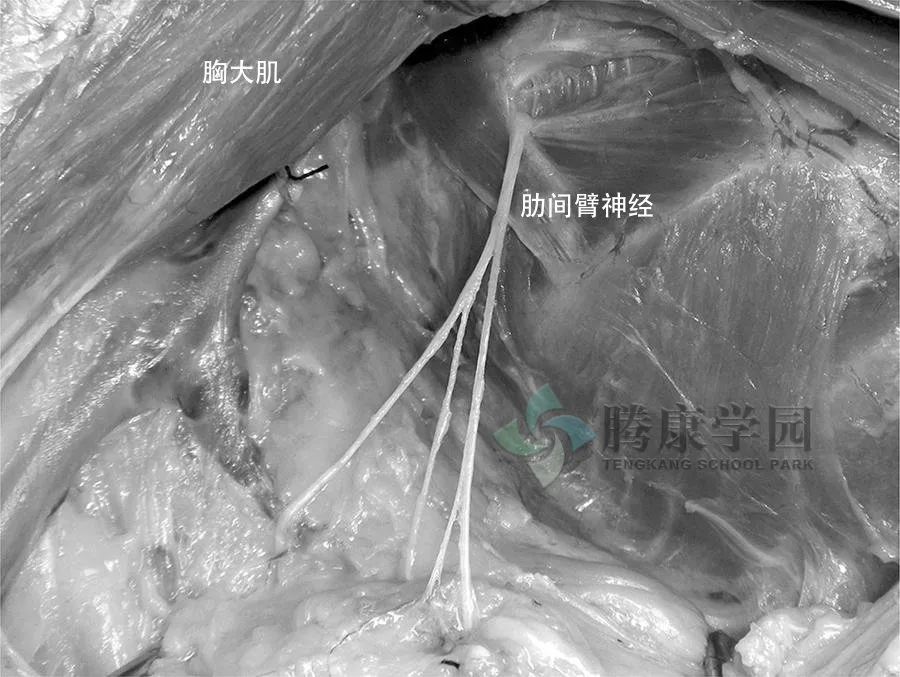
肋间臂神经是纯感觉神经,主要来自第二肋间神经 (T2),偶尔来自 T3。因此,肋间臂神经不是臂丛神经的组成部分。肋间臂神经平行于腋静脉,在垂直方向上的距离约为 1.5 cm。
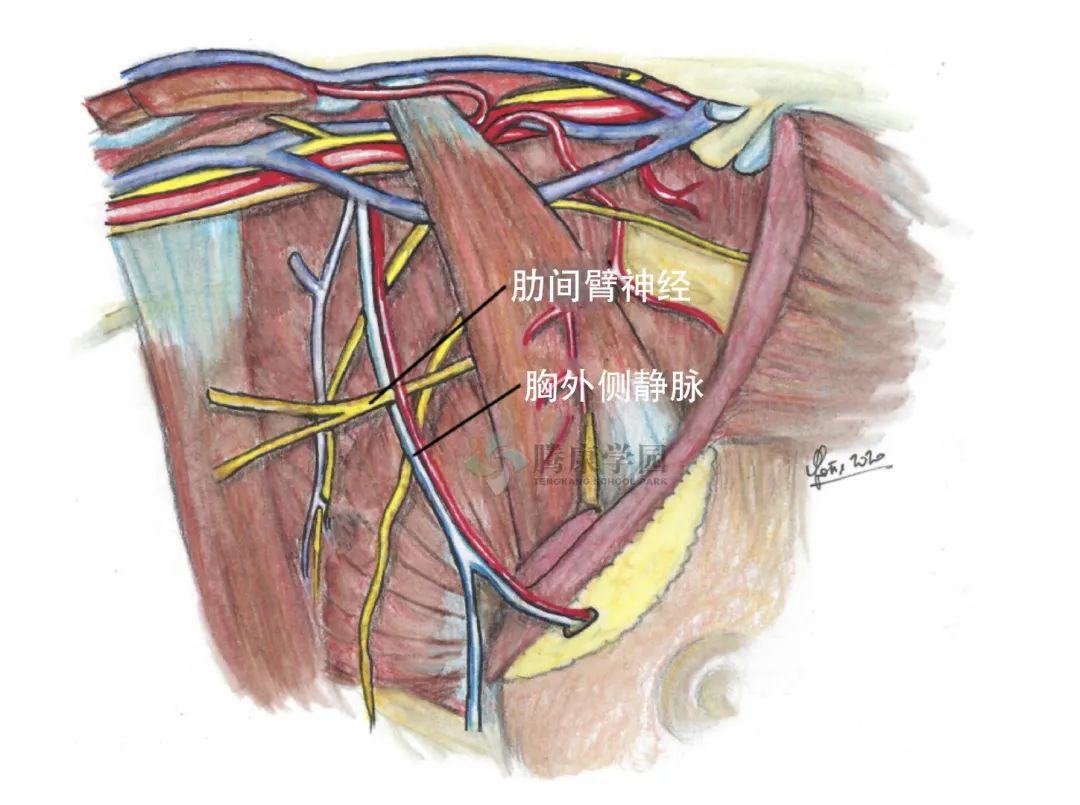
穿过腋窝时,神经发出腋后支,供应腋后皱襞。此后,肋间臂神经刺穿深筋膜并供应手臂内侧和后部上半部分的皮肤,与桡神经后皮支相连。它的大小与内侧皮神经的大小成反比。
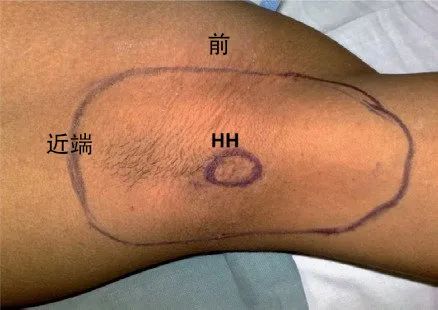
肋间臂神经阻滞后 10 分钟感觉阻滞分布的图示
HH为覆盖肱骨头内侧的皮肤中点
在朝向内侧臂的过程中,它穿过腋窝,从而在常见的腋窝手术中增加医源性损伤的风险。
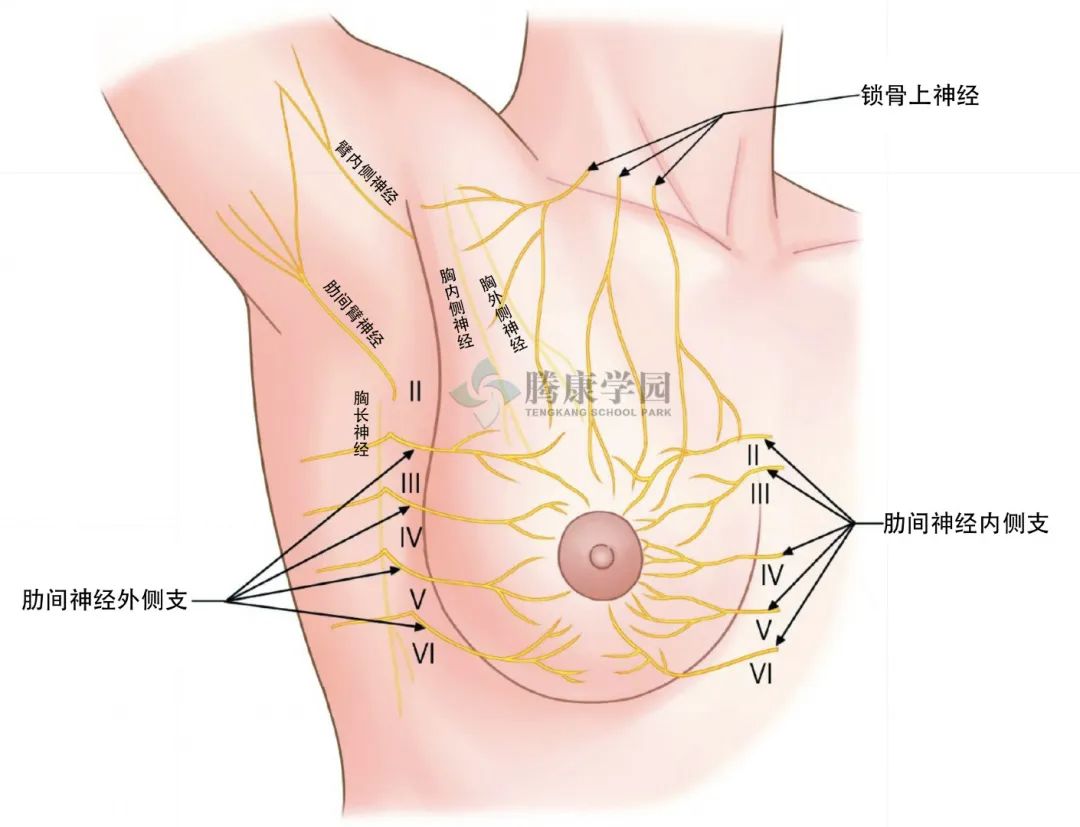
肋间臂神经的结构本质上是高度可变的,具有众多起源、分支模式和通信分支。肋间臂神经存在于 98.4% 的人中。
它最常见(90.6%)起源于 T2 水平的纤维,并且通常以两种分支模式走行:在 47.0% 的病例中作为单一主干,在 42.2% 的病例中作为分叉模式。在后一种情况下,分叉通常不相等(63.4%)。
此外,肋间臂神经在 41.3% 的病例中呈现与臂丛神经的吻合通信。
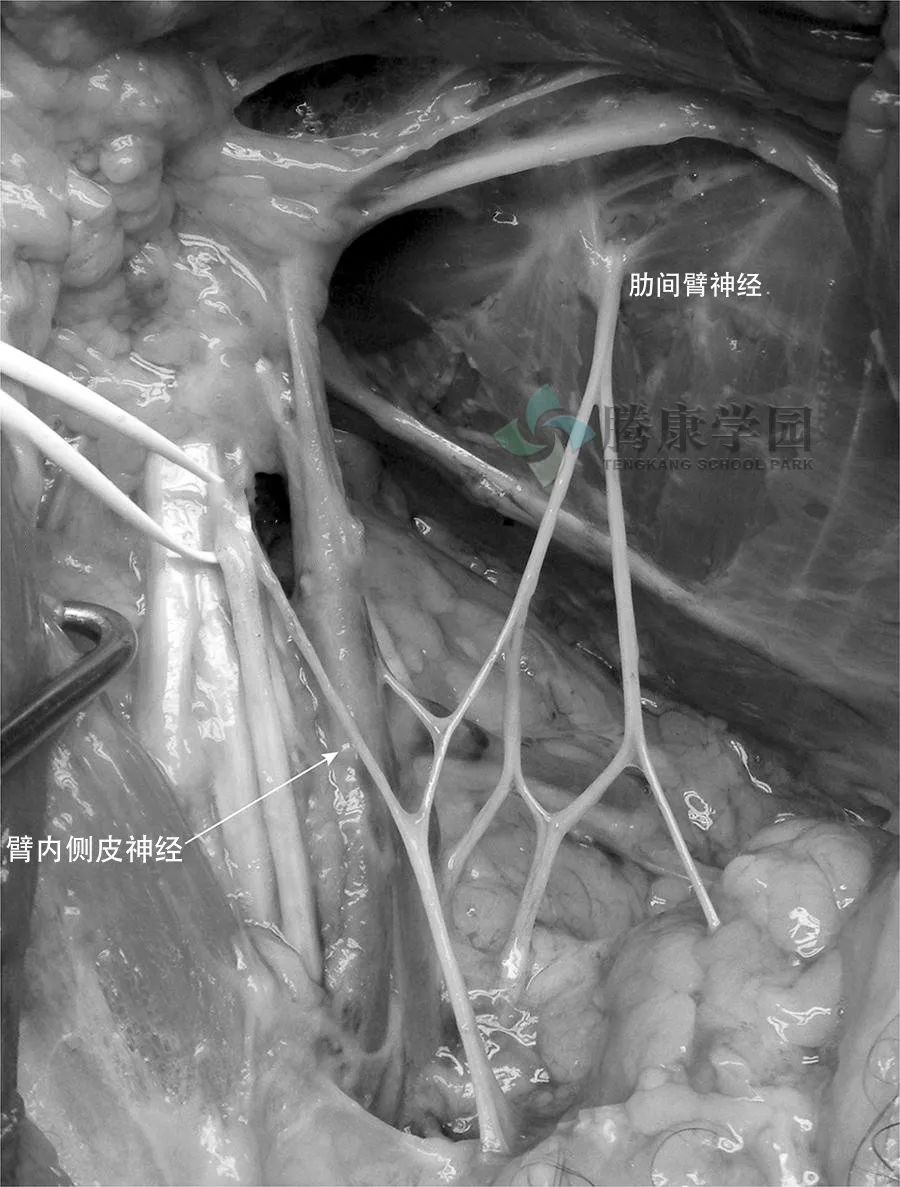
肋间臂神经的医源性损伤在涉及腋窝的外科手术中最为常见。
值得注意的是,乳腺癌手术,尤其是出于诊断和治疗原因,会增加肋间臂神经对损伤的易感性。
神经损伤或刺激可能因器械创伤而发生,例如来自牵开器的长时间压力或通过电灼和钝性解剖直接切断。术后瘢痕组织、感染、血肿和蜂窝组织炎是可引起肋间臂神经分布疼痛的其他因素。
总结
肋间臂神经是第二肋间神经的一条皮神经,并为腋窝、上内侧臂和上外侧胸部的一小块区域提供感觉供应,常在腋窝手术中受到医源性损伤,造成患者主诉疼痛、麻木或刺痛,并在夜间加重并伴有上肢运动受限或疼痛加剧。
参考文献
-
Henry BM, Graves MJ, Pękala JR, et al. Origin, Branching, and Communications of the Intercostobrachial Nerve: a Meta-Analysis with Implications for Mastectomy and Axillary Lymph Node Disp in Breast Cancer. Cureus. 2017;9(3):e1101. Published 2017 Mar 17. doi:10.7759/cureus.1101
-
Rustagi SM, Sharma M, Singh N, Mehta V, Suri RK, Rath G. Peripheral communications of intercostobrachial nerve Peripheral communications of the intercostobrachial nerve in relation to the alar thoracic artery. Adv Biomed Res. 2015;4:51. Published 2015 Feb 17. doi:10.4103/2277-9175.151555
-
Thallaj AK, Al Harbi MK, Alzahrani TA, El-Tallawy SN, Alsaif AA, Alnajjar M. Ultrasound imaging accurately identifies the intercostobrachial nerve. Saudi Med J. 2015;36(10):1241-1244. doi:10.15537/smj.2015.10.11758
-
Huang S, Qiu P, Chen W, Zhang Y, Luo K, Li J. Modified radical mastectomy for anterior thoracic nerve and intercostobrachial nerve protection (case report). Gland Surg. 2020;9(2):463-466. doi:10.21037/gs.2020.02.17
-
Chang PJ, Asher A, Smith SR. A Targeted Approach to Post-Mastectomy Pain and Persistent Pain following Breast Cancer Treatment. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(20):5191. Published 2021 Oct 16. doi:10.3390/cancers13205191
-
Henry BM, Graves MJ, Pękala JR, Sanna B, Hsieh WC, Tubbs RS, Walocha JA, Tomaszewski KA. Origin, Branching, and Communications of the Intercostobrachial Nerve: a Meta-Analysis with Implications for Mastectomy and Axillary Lymph Node Disp in Breast Cancer. Cureus. 2017 Mar 17;9(3):e1101. [PMC free article]
-
Loukas M, Hullett J, Louis RG, Holdman S, Holdman D. The gross anatomy of the extrathoracic course of the intercostobrachial nerve. Clin Anat. 2006 Mar;19(2):106-11.
-
Kasai T, Yamamoto N. [Medial brachial cutaneous nerves and the intercostobrachial nerves]. Kaibogaku Zasshi. 1966 Feb 01;41(1):29-42.